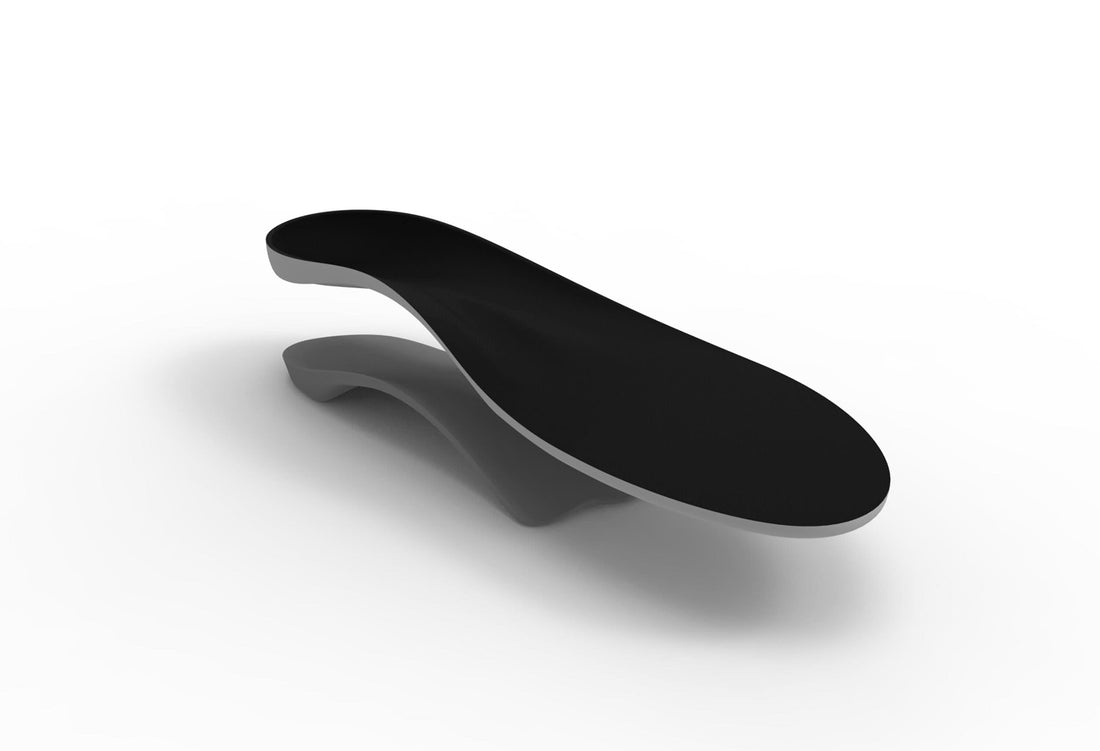
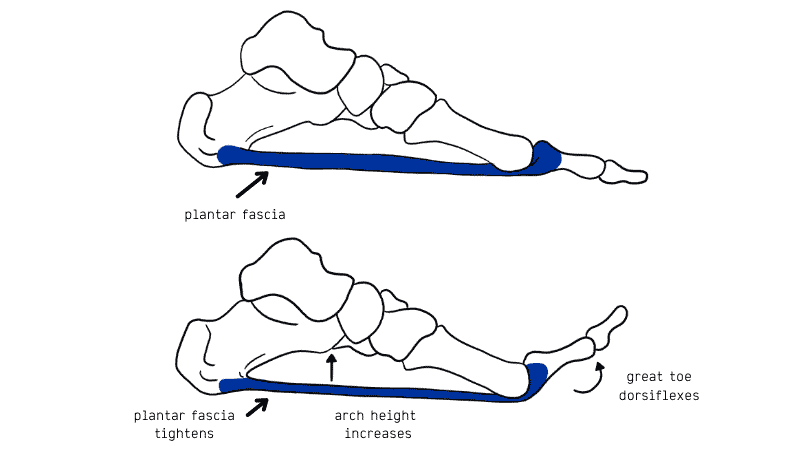
The Hubscher Manoeuvre or Jack’s Test is a method of evaluating the flexibility of a pes cavus. It is also used to determine the timing and force needed to initiate Windlass.
The test is performed with the patient weight bearing while the clinician dorsiflexes the hallux and watches for the formation of an arch.
Results
Positive: Arch formation or results from the flatfoot being flexible.
Negative: Lack of arch formation or results from the flatfoot being rigid.
Orthotic Adjustment
If test shows;
Delayed timing: add padding under the Hallux and/or use a heel raise.
High force for flexion of the Hallux: use a 1st Ray Cut Out.
Notes
The clinician should also note how soon after dorsiflexion of the Hallux the arch forms and the tibia externally rotates. If arch formation is delayed this implies an inefficient Windlass system.
About Interpod’s Biomechanical Tests
Interpod utilises the most current biomechanical tests to aid with orthotic prescription. The following relevant biomechanical tests will help practitioners maximise patient outcomes.
The purpose of a biomechanical test is to determine if patient symptoms are mechanical in nature or whether they are caused by other factors such as illness. The results of a biomechanical test can be used to highlight the pathomechanics of patient symptoms. In addition, they can be used to determine the most appropriate orthotic and possible orthotic additions if required.