The Good Old Days
Historically, foot orthotics were prescribed visually, aligning the foot to subtalar joint neutral. We now understand more about forces and how the position of the subtalar joint axis effects effort. A medial placed subtalar joint axis has a longer lever arm and pronates with greater force than a lateral axis increasing tissue strain and risk of injury.
New Prescription Method
The foot pronates then supinates. Interpod orthotics resist the force of pronation and assist the foot to supinate. By using the Keystone you can measure the force of pronation/ supination and determine with clinical experience prescribe the amount of rearfoot wedge/ arch height and material stiffness needed from the orthotic.
-
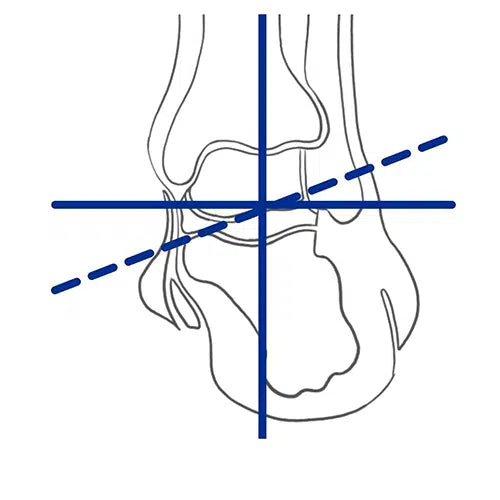
Pronation
If the pronation force is too great injury occurs. This is often the case with a medial subtalar joint axis. Effective orthotics resist the force of pronation
-
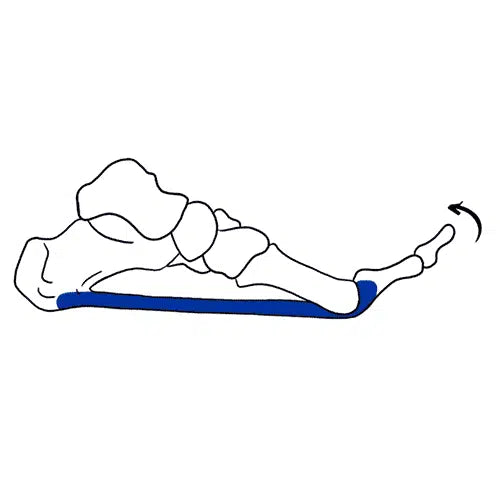
Supination
Enabling the 1st Ray to plantar flex stabilizes propulsion. Effective orthotics assist the 1st Ray to plantar flex.
Interpod use these design features to resist pronation and assist supination
-
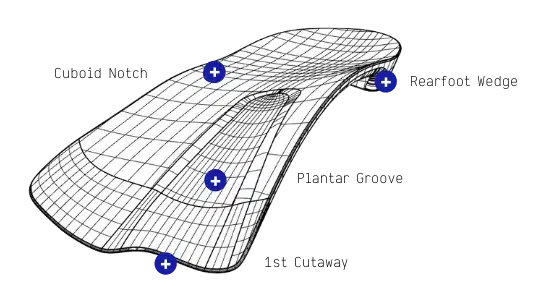
Features that assist supination
-
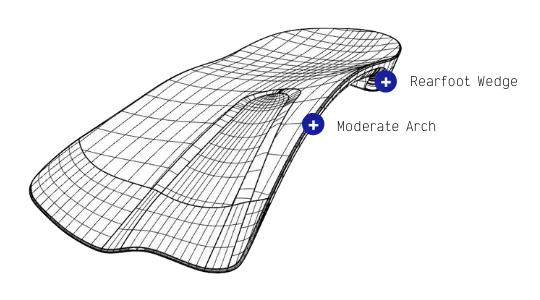
Features that resist pronation







