The Supination Resistance Test and Its Role in Biomechanics
Study by: Gabriel Moisan, Dominic Chicoine, Sean McBride, Nader Farahpour, Pier‑Luc Isabelle, Camille Dagenais and Ian Grifths
View original study
Download pdf of study
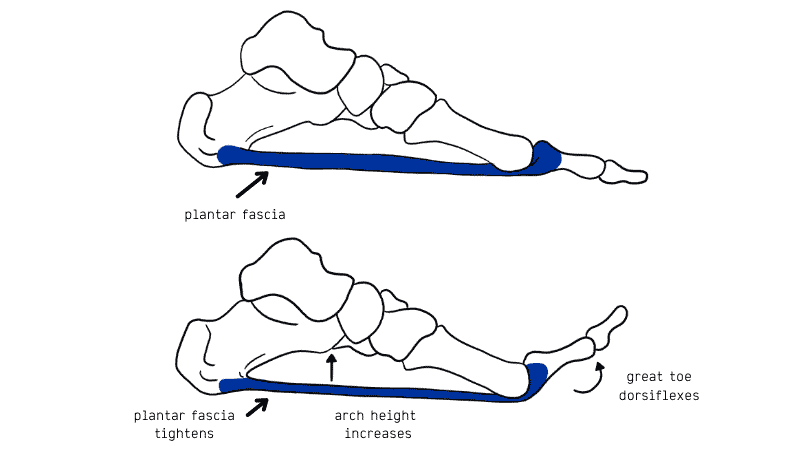
When it comes to foot and ankle biomechanics, one key diagnostic tool that helps both clinicians and researchers understand movement patterns is the Supination Resistance Test (SRT). This test evaluates how much force is required to supinate the foot—essentially measuring its resistance to rolling outward. A recent study explores how this test correlates with lower limb biomechanics and the effectiveness of foot orthoses in individuals with Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD).
What is Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction (PTTD)?
PTTD is a progressive condition affecting the posterior tibialis tendon, often leading to foot pain, arch collapse, and difficulty walking. It primarily affects older adults and can significantly impact daily activities. Given that foot orthoses (FOs) are often prescribed to alleviate symptoms, understanding their biomechanical effects is crucial.
Key Findings on the Supination Resistance Test
A study involving 21 individuals with Stage I or II PTTD examined the reliability of the Supination Resistance Test and its ability to predict foot and ankle mechanics. The key takeaways include:
-
The SRT showed excellent reliability, making it a strong clinical tool for assessing foot biomechanics.
-
There was a direct correlation between SRT results and midfoot/ankle movements, indicating that higher supination resistance is linked to greater foot pronation.
-
The test also helped predict the effectiveness of foot orthoses in modifying foot mechanics.
The Effect of Foot Orthoses on Biomechanics
Participants wore custom-made foot orthoses (FOs) for two weeks before undergoing gait analysis. The study found that:
-
Foot orthoses significantly reduced ankle eversion angles and inversion moments, providing mechanical support for individuals with PTTD.
-
Those with lower supination resistance showed better responses to orthoses, making the SRT a useful predictive tool.
Why This Matters for Clinicians and Patients
For healthcare providers, the Supination Resistance Test offers a quick and effective way to assess biomechanical deficiencies in individuals with PTTD. It also assists in determining who will benefit most from foot orthoses, leading to better treatment outcomes.
For patients, understanding the importance of foot mechanics and early intervention can help prevent the progression of PTTD and ensure better mobility and comfort.
Final Thoughts
The Supination Resistance Test is more than just a diagnostic tool—it provides valuable insights into foot biomechanics and the effectiveness of orthotic interventions. By incorporating this test into clinical assessments, practitioners can make more informed decisions and improve patient outcomes for those dealing with PTTD and other foot-related issues.
Have you experienced foot pain or arch issues? Get in touch to see if foot orthoses might be a good solution for you.