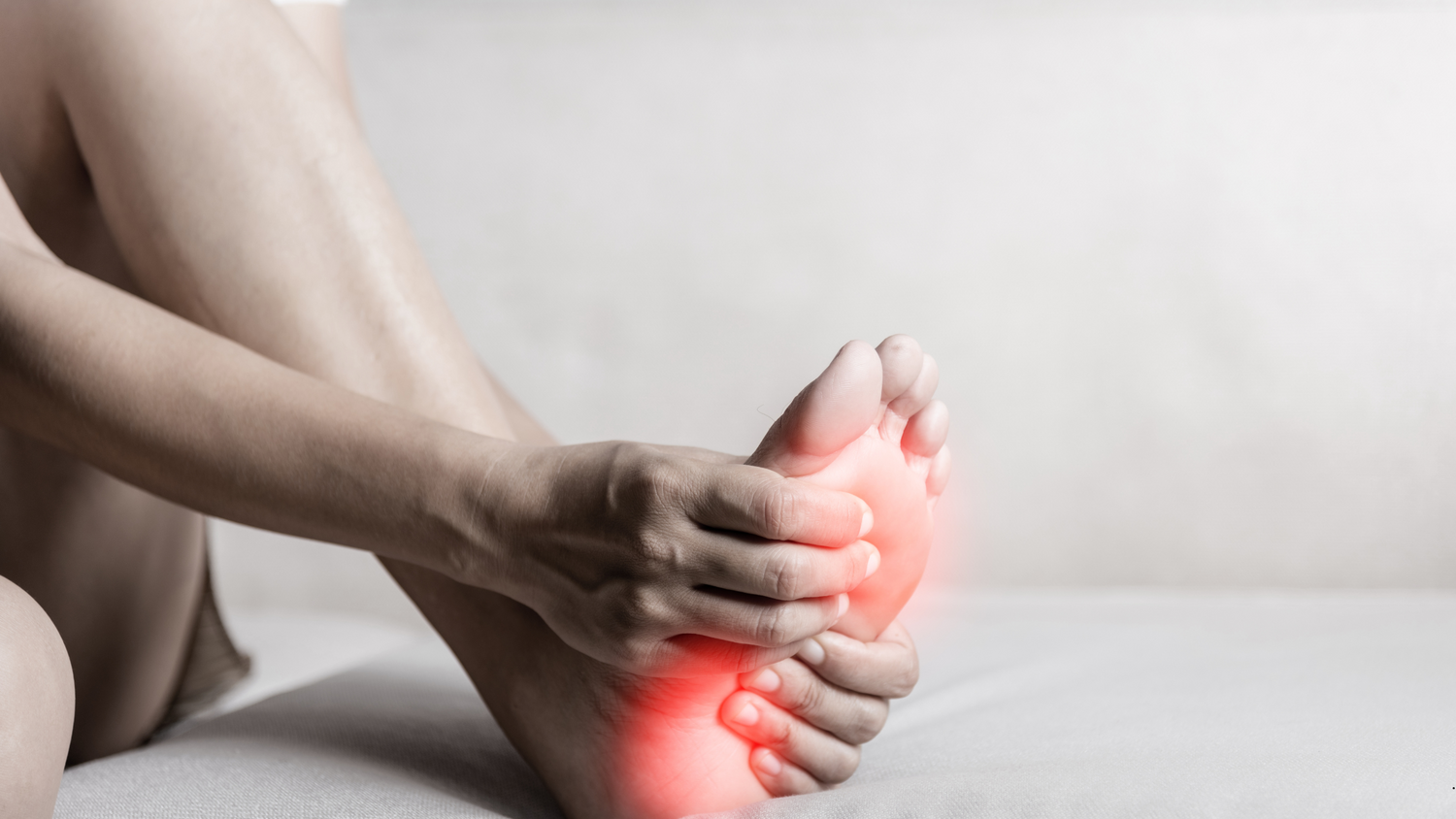
Bursas are fluid filled sacs located between bone, muscles, tendons and skin. A bursa’s function is to reduce pressure and friction between these tissues by providing cushioning and lubrication during movement. When a bursa is irritated or inflamed causing pain, this is known as bursitis. Bursitis can occur in various places throughout the body such as the forefoot, heels, knees, hips, and shoulders.
Cause
Excessive use of muscles and joints may irritate a bursa, therefore resulting in bursitis.
A sudden increase in activity level may put abnormal stress on a bursa.
Abnormal biomechanics resulting in abnormal muscle function can cause irritation of a bursa.
Excessive pressure on a joint or tendon may result in bursitis, such as pressure on the forefoot or heel when walking bare foot.
Excessive weight may also put increased stress on joints and muscles.
Symptoms
- Pain and swelling at the site of a bursa.
- Loss of range of motion of a joint involved with the bursa.
- Visible redness and inflammation at the painful site.
- Pain on physical palpation at the site of the bursa.
- Increased temperature or a feeling of warmth around the painful area.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Bursitis can be made by your health practitioner and is based on the following:
- Assessment of the level of activity currently being undertaken.
- Physical examination and palpation of the painful site.
- Assessment of biomechanics and joint function.
- Diagnostic ultrasound, or MRI, can reveal bursitis.
- Assessment of medical history and history of bursitis.
Treatment
- Orthotics: Interpod orthotics may assist bursitis in the feet, knees and hips by providing support for the feet, and correct any biomechanical abnormalities of the knees and hips that are causing the bursitis.
- Ice: Icing the painful area may assist in temporary pain relief.
- Pain relief medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen can reduce inflammation from the bursitis.
- Regular stretching: Stretching or strengthening as advised by your practitioner may improve joint function and biomechanics.
- Footwear: Shoes that are supportive and cushioned may improve joint function.
- Rest: Resting the painful site can reduce pain.
- Surgery: Surgical removal of the painful bursa is a last resort treatment when all other treatments have failed.
Prevention
- Orthotics: Continue to wear your Interpod orthotics for work and exercise to maintain foot function, correct biomechanics and posture which wil prevent bursitis from occurring.
- Footwear: Select suitable shoes at work and supportive runners for sport may prevent abnormal biomechanics.
- Activity level: A gradual, rather than a sudden increase in activity level may prevent bursitis from occurring.
- Stretching: Regular stretching before and after activities can maintain joint range of motion, and prevent irritation of a bursa.
References
https://www.webmd.com/pain-management/arthritis-bursitis
https://www.mayoclinic.com/health/bursitis/DS00032
https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/bursitis.html
Frowen, O’Donnell, Lorimer & Burrow. (2010). Neale’s Disorders of the foot (8th Ed.), Elsevier Limited, pg. 30.